
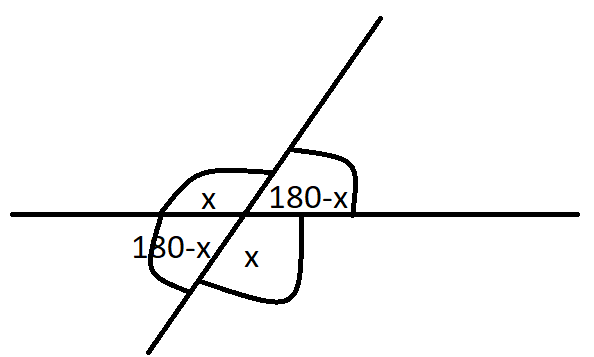
These intersecting lines are a linear pair since their angles equal 180 degrees when added together. Perpendicular lines intersect and form a 90-degree angle at the point where they meet. Parallel lines and line segments run side by side in a plane and never intersect. Rays start at a single point and extend infinitely in a single direction. Line segments have end points, which are points along the line. Supplement Theorem If two angles form a linear pair. They have arrows denoting their infinite nature. Linear Pair two adjacent angles whose non-common sides form opposite rays (form a straight angle).
#Linear pair postulate definition geometry series#
A series of points that extend indefinitely form a line. Understanding lines is a vital skill in the study of geometry. Overlapping Angles Theorem: Given
#Linear pair postulate definition geometry full#
An angle reaches full rotation at 360 degrees. There are also angles with a space greater than 180 degrees called reflex angles. Obtuse angles measure greater than 90 degrees. A straight angle (also known as a straight line) measures 180 degrees, and a right angle measures 90 degrees. Mathematicians measure angles in degrees, and this measurement defines the type of angle. When two lines, line segments or rays intersect, they create spaces called angles. Postulates like the linear pair postulate can be used in geometric proofs and mentioned in the justification section of the proof. The proof traces the series of facts, deductions and logic that support the final conclusion. In geometry, a proof is an argument that confirms or disproves a statement. It is possible to prove the statement “If two lines intersect, then they intersect in exactly one point.” Both postulates and theorems can be used to prove statements related to geometry. A theorem is a true statement that one can prove. For example, mathematicians believe the statement “through any two points there is exactly one line” despite the fact that it is not proven. Postulates are statements that have not been proven but are assumed to be true. The fifth postulate remains unproven despite several attempts over the years to prove it. Another asserts that all right angles are congruent. The second states that one can extend a straight line continuously. The first postulate states that it’s possible to draw a straight line between any two points. There are five geometric postulates explained in the book. His book, “Elements,” details 465 theorems and proofs that created the foundation of geometry as it’s studied today.
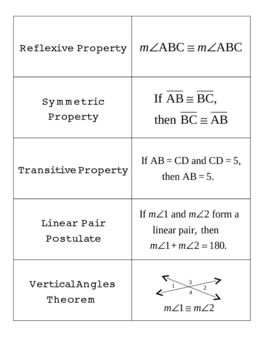

If you know the measures of one of the angles formed when two lines intersect, then you know the measures of all four angles. Two vertical angles are always opposite congruent angles, one of these angles belongs to a linear pair of angles. Definition of Supplementary Angles Supplementary angles are two angles with. A linear pair of angles are always adjacent angles that add up to 180°. Linear Pair Theorem If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary. Most of these will be proven using the SAS postulate. Definition of Linear Pair A linear pair is a pair of adjacent angles with noncommon. You will see several theorems about isosceles triangles. As long as you are careful to discuss two sides and the included angle, you'll be fine. The sides that include these angles are ¯MN and ¯PN (for QNP).
Notice that the angles you are focusing on are MNP and QNP. Use the reflexive property of ~= to obtain another set of congruent sides: A side is congruent to itself. The congruence of one set of sides is given. Because ¯PN ¯MQ, you know that right angles are formed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
